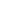
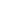China launched its self-made "Haiyang-1B" oceanic survey satellite from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center in Shanxi Province at 11:27 am Wednesday, April 11, 2007. Apr.11 - China successfully launched its second oceanic survey satellite "Haiyang-1B" (Ocean 1B) from Taiyuan Satellite Launching Center on Wednesday.
The China-made satellite was launched at 11:27 a.m. and reached the target orbit aboard a Long March-2C carrier rocket, China's most senior ocean research official said.
The "Haiyang-1B", a crucial component of China's three dimensional oceanic survey system, would be used to monitor the color and temperature of the ocean, said Sun Zhihui, director of the State Oceanic Administration.
The satellite would aid China's development and utilization of oceanic resources, construction of ports, monitoring and prevention of oceanic pollution, resource investigation and the development of coastal areas as well as for study of global environmental changes, he said.
China launched its first oceanic survey satellite "Haiyang-1A" in May 2002 to monitor ocean color and temperature using remote sensing technology
"Haiyang-1A" monitored the Bohai Sea, the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea and the South China Sea.
Chief scientist Bai Zhaoguang said the "Haiyang-1B" is an upgraded version of the earlier model.
"The operational life of 'Haiyang-1B' is expected to reach three years, a year longer than 'Haiyang-1A'. The new satellite provides three times as much information," he said.
"The satellite's observational devices now have a 3,000-kilometer range -- up from 1,300 kilometers -- and its imaging devices provide higher resolution photography," he added.
Haiyang-1B had a stronger structure than Haiyang-1A, enabling it to withstand stronger shocks and jolts, he said.
Bai said the Haiyang-1B had software and Internet capabilities that allowed it to repair itself in space, saying 10 computers worked together to repair the spacecraft in the event of a technical breakdown.
The breakdown of a solar cell driver shortened Haiyang-1A's operational life. But Haiyang-1B's improved technology would enable it to solve this kind of problem by itself, Bai said.
The "Haiyang-1A", China's first experimental satellite to use ocean color detecting, worked for 685 days from May 2002 to April 2004 with an operational life shorter than the designed lifespan of two years.
During its operation, it completed 1,830 surveys and provided oceanic information for 126 users including the oceanic administration, producers of oceanic products, research institutes and universities.
SOA director Sun Zhihui said China would develop five more oceanic satellites in the medium term, saying satellites were urgently needed to develop the country's marine economy, provide a marine early warning system and safeguard the nation's maritime rights.
"Haiyang-1B" is developed by the China Academy of Space Technology of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp (CASTC). It was launched on the 96th flight of a Long March carrier rocket, which was developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology of the CASTC.